Join More Than 50,000+ Subscribers and get latest camera news and rumors
NEW CAMERA VIDEOS ON YOUTUBE
|
By admin, on June 6th, 2025

Sony A7 IV open box camera with its 28 to 70 mm kit lens is available at a discounted price. The camera is used only for display purposes for the customer. Open box camera bodies and lenses are generally in completely mint condition, yes, you may find some fingerprints on the body. Also, when you purchase this camera, you get a free 1-year protection warranty from Hyderabad, which can be extended if you wish to with an additional cost.
Click here to see the Sony A7 IV Camera open box deal at Adorama.com
Also see – Nikon Z5 Mirrorless at $799 (Refurbished by Nikon USA)
Follow us for more updates and get LIVE RUMORS –> FACEBOOK | TWITTER | INSTAGRAM to get live news — > get live camera news + –> See More+ Explore more Open Box Camera Deals and Camera Deals USA
By admin, on May 29th, 2025

The Sony FX2 is an extended version of the Sony A7 IV, optimised for its maximum cinematography specifications. So hardware-wise, both the cameras are the same — is it true? NO, we do have some sort of advancement in the hardware part, and the advancement is the introduction of the AI chip, which was absent in the Sony A7 IV, as well as the very unique tiltable electronic viewfinder design. So let’s explore the differences between the two.
Design Comparison
| Feature |
Sony A7 IV |
Sony FX3 |
| Lens Mount |
Sony E |
Sony E |
| Material |
Magnesium Alloy |
Magnesium Alloy |
| Dimensions (W x H x D) |
5.2 x 3.8 x 3.1″ (131.3 x 96.4 x 79.8 mm) |
5.1 x 4.1 x 3.1″ (129.7 x 103.7 x 77.8 mm) |
| Weight |
1.4 lb (658 g, with battery and media) |
1.5 lb (679 g, with battery and media); 1.3 lb (594 g, body only) |
| Media Slots |
Slot 1: CFexpress Type A / SD (UHS-II); Slot 2: SD/SDHC/SDXC (UHS-II) |
Slot 1: CFexpress Type A / SD (UHS-II); Slot 2: SD/SDHC/SDXC (UHS-II) |
| Video I/O |
1x HDMI Output |
1x HDMI Output, 1x USB-C 3.0/3.1/3.2 Gen 1 Output / Lightspeed 10 Gbps |
| Audio I/O |
1x 3.5 mm TRS Stereo Mic Input, 1x 3.5 mm TRS Stereo Headphone Output |
1x 3.5 mm TRS Stereo Mic Input, 1x 3.5 mm TRS Stereo Headphone Output / XLR input |
| Other I/O |
1x Sony Multi/Micro-USB, 1x USB-C (USB 3.2 Gen 1) |
1x Micro-USB, 1x USB-C |
| Wireless |
Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n), Bluetooth 4.1 |
2.4/5 GHz Wi-Fi (802.11a/b/g/n/ac), Bluetooth 5.0 |
| Mobile App |
Creators’ App (Android/iOS) |
Sony Creators’ App (Android/iOS) |
| GPS |
Yes, via a connected smartphone |
No |
| Display |
3.0″ Free-Angle Tilting Touchscreen LCD, 1,036,800 Dot |
3.0″ 180° Tilting Touchscreen LCD, 1,036,800 Dot |
| Viewfinder |
Electronic (OLED), 0.5″, 3,680,000 dots, 0.78x magnification / Tiltable EVF |
Electronic (OLED), 3,686,400 Dot (no size/magnification specified) |
| Shoe Mount |
1x Intelligent Hot Shoe |
1x Intelligent Hot Shoe |
| Tripod Mount |
1x 1/4″-20 Female (Bottom) |
2x 1/4″-20 Female (Bottom), 3x 1/4″-20 on Camera Body |
| Battery |
NP-FZ100, ~520 shots |
NP-FZ100, power consumption ≤6.6 W |
| Operating Conditions |
32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C) |
32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C) |

What advantages do we have in the new Sony FX2 camera over the Sony A7 IV?
- It looks like a cinema camera, but it has a very deep hand grip and a very innovative tiltable electronic viewfinder.
- Additionally, we have an option in FX2 to use an XLR handle for the body part, and with that grip, we can add 32-bit audio to our videos.
- An option to record DCI 4K instead of UHD 4K in the new Sony FX2 camera with lots of custom LUTs as well as an option of extended dual native ISO range, resulting in 15 stops of DR performance.
- 30% increase in the AI autofocus performance of the new Sony FX2 camera compared to the Sony A7C Mark II or the A7 Mark IV camera.
- 16-bit RAW video recording is an option available via the HDMI port. Obviously, the Sony A7 Mark IV camera remains limited to 10-bit video.
- Introduction of active stabilisation mode as well as frame stabiliser — both of these are not in the way they should be in the Sony A7 Mark IV due to the absence of the dedicated AI chip inside the body.
- Support for anamorphic lenses and in-camera de-squeeze functionality for the recorded footage.
- Built-in internal fan to manage any sort of overheating issue if required.
Photography Comparison
| Feature |
Sony A7 IV |
Sony FX2 |
| Sensor Resolution |
Actual: 34.1 MP, Effective: 33 MP (7008 x 4672) |
Actual: 34.1 MP, Effective: 33 MP |
| Image Sensor |
35.9 x 23.9 mm Full-Frame CMOS |
35.9 x 23.9 mm Full-Frame CMOS |
| Image Stabilization |
Sensor-Shift, 5-Axis |
Sensor-Shift, 5-Axis |
| ISO Sensitivity |
Photo: 100-51,200 (50-204,800 Extended); Auto: 100-12,800 |
Photo: 100-51,200 (50-204,800 Extended), Dual Base: 800/4000 |
| Shutter Speed |
1/8000 to 30s, Bulb Mode |
1/8000 to 30s (Photo Mode) |
| Metering Method |
Center-Weighted, Highlight Weighted, Multi-Zone, Spot |
Center-Weighted, Highlight Weighted, Multi-Zone, Spot |
| Exposure Modes |
Aperture Priority, Auto, Manual, Program, Shutter Priority |
Aperture Priority, Auto, Manual, Program, Shutter Priority |
| White Balance |
2500-9900K, Multiple Presets |
2500-9900K, Multiple Presets |
| Continuous Shooting |
Up to 10 fps for 1000 frames (Raw, JPEG) |
Up to 10 fps for 1000 frames (Raw, JPEG) |
| Autofocus Points |
Phase Detection: 759, Contrast Detection: 425 |
Phase Detection: 759 (Photo), 627 (Video) |
| Autofocus Sensitivity |
-4 to +20 EV |
-4 to +20 EV |
Sony FX2: Built for Filmmakers
The Sony FX2 isn’t just another camera—it’s a Cinema Line powerhouse tailor-made for both aspiring cinematographers and seasoned content creators. Under the hood, it shares the same 33 MP sensor as the A7 IV, but in S-Log3 it unlocks up to 15 stops of dynamic range, giving you richer highlights and deeper shadows. Here are the standout video features you’ll love:
-
Tilting EVF: A 3.68 million-dot viewfinder that flips up 90°—perfect for shooting low or high without cramping your style.
-
Video-First Layout: Large, easy-to-find record button, full-size HDMI, plus intuitive shutter-angle control so you can dial in cinematic motion blur on the fly.
-
AI Power: Thanks to its onboard AI chip, autofocus is 30% snappier, and you get nifty tools like Auto-Framing and the Framing Stabilizer—ideal for run-and-gun solo shoots.
The one caveat? If you were hoping for full-frame 4K at 60 fps, you’ll find the FX2 capped at Super 35 crop at that frame rate—unlike its cousin, the FX3.
Sony A7 IV: The Hybrid Powerhouse
If you wear two hats—photographer by day, videographer by night—the A7 IV is your Swiss Army knife. Its 33 MP sensor churns out gorgeous JPEGs and HEIFs, and its video chops are nothing to sneeze at. Here’s why so many hybrid creators can’t put it down:
-
Stills & Motion: Capture high-res stills in Log, plus reliable autofocus that tracks fast-moving subjects with ease.
-
Flexible Design: Dual card slots and a fully articulating 1.03 million-dot touchscreen let you work confidently in any scenario.
-
Budget-Friendly: At $2,498, it undercuts the FX2 while still offering professional-level performance.
The trade-off? You don’t get the FX2’s video-optimized menus or dedicated cinema-grade controls like shutter-angle adjustment.
Video Comparison
| Feature |
Sony A7 IV |
Sony FX2 |
| Internal Recording Modes |
H.264/XAVC S-I 4:2:2 10-Bit: UHD 4K up to 60 fps [240-600 Mb/s]; H.265/XAVC HS 4:2:2/4:2:0 10-Bit: UHD 4K up to 60 fps [50-200 Mb/s]; 1080p up to 100 fps |
H.264/XAVC S-I 4:2:2 10-Bit: DCI 4K/UHD 4K up to 60 fps [240-600 Mb/s]; H.265/XAVC HS 4:2:2/4:2:0 8/10-Bit: UHD 4K up to 60 fps [30-200 Mb/s]; 1080p up to 120 fps |
| External Recording Modes |
4:2:2 10-Bit/4:2:0 8-Bit via HDMI: UHD 4K up to 60 fps, 1080p/i up to 60 fps |
4:2:2 8/10-Bit via HDMI: DCI 4K/UHD 4K up to 60 fps, 1080p up to 60 fps; Raw 16-Bit: 4672 x 2628 up to 60 fps |
| Gamma Curve |
HDR-HLG, Sony S-Log 2, Sony S-Log 3 |
HDR-HLG, Rec709, S-Cinetone, Sony S-Log 3, Standard |
| User |
|
|
| Dynamic Range |
Not specified |
15 Stops |
| Anomorphic lenses support |
No |
Yes |
| Fast-/Slow-Motion |
Yes |
Yes |
| Built in Fan |
No |
Yes |
| Overheating issues |
Yes, when used for a prolonged period in the summer season |
None |
| Recording Limit |
No |
No |
| IP Streaming |
No |
RTMP, RTMPS, SRT (720p to 4K at 25p-59.94p) |
| Audio Recording |
XAVC S: 2-Channel 16-Bit 48 kHz LPCM; MPEG4: 2-Channel AAC LC |
2/4-Channel 24-Bit 48 kHz LPCM; 2-Channel 16-Bit 48 kHz LPCM |
| Shutter Speed (Video) |
1/8000 to 1/4s |
1/8000 to 1s |
| Autofocus Points (Video) |
Phase Detection: 759, Contrast Detection: 425 |
Phase Detection: 759 / 30% More improved AF performance due to AI chip |
So these are the major differences we have between these two cameras. Yes, many minor differences also exist between the two. But without a doubt, if you are a cinematographer or a content creator who loves to have a dedicated professional cinematography camera in his or her hand, without a doubt, the new Sony FX2 is one of the best cameras.
By admin, on May 26th, 2025
Nikon Z5 II is an entry-level camera, and Sony A7 IV is a semi-professional full-frame camera. The Sony A7 IV camera was announced on October 21, 2021. And if you compare with the Nikon Z5 II, it has been almost 3.5 years of gap between the two cameras, so despite of being an entry-level camera, the Nikon Z5 II has arrived with really advanced core specifications and it looks very competitive.
Price Difference Between the Sony A7 IV and the Nikon Z5 II
The other good thing that we generally see at first is the price difference, even before the specification, current status of both the cameras by applying all the possible discounts:
Sony A7 IV Price – $2498
Nikon Z5 II Price – $1696
So, we do have a good price difference between the two cameras.
And the amount of money we are saving in the Nikon Z5 II body, we can get lenses like Nikkor 50 mm 1.8, Nikkor 28 mm f/2.8 or Viltrox 85mm f/1.8 Z.
Now let’s talk about the design difference, the difference we have in the photographic features of both cameras and finally the video core specs difference.
Best camera design-wise:
Nikon has been creating their DSLR for decades, and their mirrorless Z5 II is very easy to hold. At the very same time, we now have a 3000-nits brightness-based electronic viewfinder which helps us to shoot even in harsh light conditions.
Sony is in its 4th generation of A7 series camera, and overall design of the camera is really very good, and the good thing is that the old menu system of the Sony has been upgraded in the A7 IV so now you don’t have to fight with the old menus in the Sony camera. So overall, the A7 IV camera design is also very appealing and usable, although about EVF screen brightness information remains uncertain. Sony hasn’t disclosed how many nits of brightness does the A7 IV EVF has.
Why do We Need a CF Express card SLot in the Sony A7 IV?
For storage purposes, the Sony A7 IV camera also features an additional CFexpress card slot inside it, but we don’t know the exact requirement of the CF card type A existence inside the Sony body since the continuous shooting speed of the A7 IV camera is limited to 10 frames per second. Even in that, the specific scenario doesn’t require that CFexpress card. And when we talk about 4K 30 APS-C crop 60fps recording, in both of these scenarios the recording resolution and bitrates match with the Nikon Z5 II, which does the everything same or even better by recording complete N-RAW video internally and providing continuous shooting speed in high resolution up to 30 frames per second in the SD card slot.
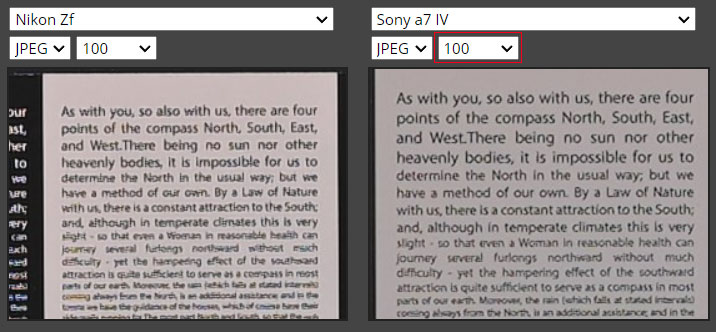
Yes, we do have a slight resolution difference between the 24 MP and 33 MP sensor, and we are going to compare both sensors here in this article and let’s find out the best sensor for you. Image credit to all tests goes to dpreview.com
Which Camera Captures the Best Images?
Yes, we do have a slight resolution difference between the 24 MP and 33 MP sensor, and we are going to compare both sensors here in this article and let’s find out the best sensor for you.
Now we have picked up the Nikon Zf camera since the Nikon Z5 Mark II uses the same sensor as the Nikon Zf, so we are comparing the Nikon sensor against the Sony A7 IV in this comparison.
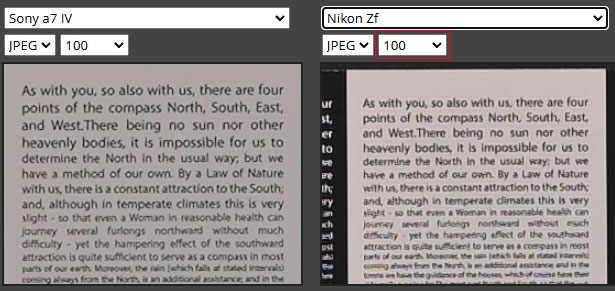
A comparison is very clear the Sony A7 IV camera is able to pick a bit more detail due to a slightly higher-resolution sensor, so if you are into commercial photography or need large prints,
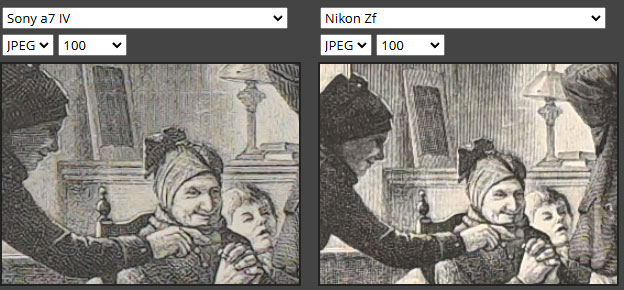
But this is not always the case. In some of the specific spots of the image, we have witnessed that the Nikon Zf / Z5 Mark II camera sensor is able to grab a bit more detail. As you can see, the pencil shading and the fine lines are more clearly visible in the samples below.
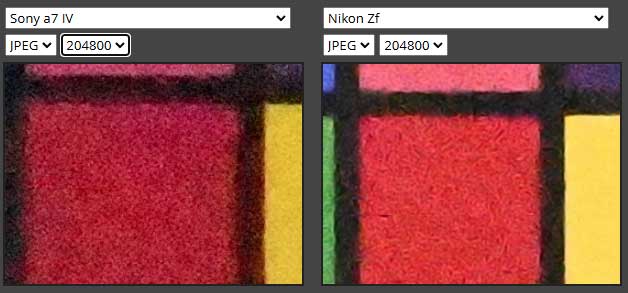
Best Camera for LOW LIGHT Photography?
The Nikon Z5 II is more suitable for low-light photography. We have to consider several factors before we judge the best camera for low-light photography. As in the comparison table, you can see that the Nikon Z5 Mark II autofocus sensitivity can go down up to -10EV, which is exceptional in this price range. At the very same time, the Nikon Z5 Mark II camera features 7.5 stops of sensor image stabilisation system, and that can be linked to the autofocus point of the camera, resulting in a highly stabilised video or still output. And at the very end, we have a 24MP BSI sensor that helps us reach the maximum potential of the camera. Combining all three factors makes the Nikon Z5 ideal in terms of low-light photography.
Best camera for wildlife photographers and sports shooters?
Nikon Z5 II is the best camera, again, and it depends on several factors. Starting from the continuous shooting speed, the Nikon Z5 Mark II camera excels. It has a maximum continuous shooting speed of up to 30 frames per second. The Sony A7 IV camera remains limited to 10fps. But that’s not the only limitation — we have again the autofocus sensitivity of the Sony A7 IV is limited, and the sensor image stabilisation of the Nikon Z5 II has become increasingly advanced. You can link the entire IBIS unit with your moving autofocus points. And at the end, if you are worried about the autofocus performance, then the Z5 II, paired up with the Expeed 7 image processor, features 9 different types of subject detection algorithms inside it. And even if you love to capture birds, the camera can do bird-eye autofocus with the latest updates.
Best camera for video?
Both of the cameras record 10-bit footage, RRS video, and 4K 60FPS video with a 1.5X crop. At the very same time, both of them can record Full HD videos at 120 frames per second. The big difference can be seen when the new Nikon Z5 Mark II camera can deliver complete RAW footage of 12-bit in your internal SD card, and the cherry-on-top thing is when you are shooting in N-Log, then you have a different set of RED LUTs available to you, which will make your entire footage more and more professional. And apart from all these, we also have vectorscope, waveforms, and timecode functionality. The Nikon Z5 Mark II camera is recommended for professional use. If you are a professional wedding cinematographer or someone who loves to capture short stories in a professional way, then the Nikon Z5 Mark II is best for you.
Sony A7 IV doesn’t support complete RAW video recording. At the very same time, the picture profiles are limited. But it does support high-quality 4K recording and S-Log, HLG support. At the very same time, the gyro-based image stabilization system helps to stabilize the footage to the maximum extent. So if you’re shooting handheld, like creating your own personal vlog, then instead of having the Nikon Z5 Mark II camera, the A7 IV will be a bit more suitable.
Best camera for longer recording
If you have to shoot podcasts, then the initial specification says the Sony A7 IV can record unlimited videos, whereas the Nikon Z5 Mark II has a 2-hour 5-minute limit, and after that, you have to start it again. Now, the concern with the Sony A7 Mark IV camera is that you have to use it in controlled weather environments and with fast V90 or CFexpress cards if you wish to record 10-bit videos for more than 1+ hour. But that’s not the case with the Nikon Z5 Mark II camera — the body is heat-resistant and supports uninterrupted recording for long periods. So you have to decide whether you want an overheating-free camera (but again, you have to restart at the 2 hour 5 minute mark), or you can deal with the Sony A7 IV if you are sitting in a controlled weather environment with air conditioners.
Specification Comparison Table Nikon Z5 II vs Sony A7 IV
| Feature |
Nikon Z5 II |
Sony A7 IV |
Design
|
| Lens Mount |
Nikon Z |
Sony E |
| Dimensions (W x H x D) |
5.3 x 4 x 2.8″ / 134 x 100.5 x 72 mm |
5.2 x 3.8 x 3.1″ / 131.3 x 96.4 x 79.8 mm |
| Weight (With Battery, Media) |
1.5 lb / 700 g |
1.4 lb / 658 g |
| Material of Construction |
Magnesium alloy/polycarbonate |
Magnesium Alloy |
| Operating Conditions |
32 to 104°F / 0 to 40°C, up to 85% humidity |
32 to 104°F / 0 to 40°C |
| Display Size |
3.2″ |
3.0″ |
| Display Resolution |
2,100,000 Dot |
1,036,800 Dot |
| Display Type |
3-Way Tilting Touchscreen LCD |
Free-Angle Tilting Touchscreen LCD |
| Viewfinder Type |
Electronic (OLED) |
Electronic (OLED) |
| Viewfinder Size |
0.5″ |
0.5″ |
| Viewfinder Resolution |
3,690,000 Dot |
3,680,000 Dot |
| Viewfinder Magnification |
Approx. 0.8x |
Approx. 0.78x |
| Viewfinder Eye Point |
21 mm |
23 mm |
| Viewfinder Diopter Adjustment |
-4 to +2 |
-4 to +3 |
| Media/Memory Card Slot |
Dual Slot: SD/SDHC/SDXC (UHS-II) |
Slot 1: CFexpress Type A / SD (UHS-II), Slot 2: SD/SDHC/SDXC (UHS-II) |
| Video I/O |
1x Micro-HDMI Output |
1x HDMI Output |
| Audio I/O |
1x 3.5 mm TRS Stereo Headphone Output, 1x 3.5 mm TRS Stereo Microphone Input |
1x 3.5 mm TRS Stereo Headphone Output, 1x 3.5 mm TRS Stereo Microphone Input |
| Other I/O |
1x 3.5 mm Remote Input, 1x USB-C (USB 3.2 / 3.1 Gen 1) Data Input/Output |
1x Sony Multi/Micro-USB Remote Input, 1x USB-C (USB 3.2 / 3.1 Gen 1) Data Input/Output |
| Wireless |
Bluetooth 5.0, 2.4 / 5 GHz Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) |
Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n), Bluetooth 4.1 |
| Mobile App Compatibility |
Yes: SnapBridge (Android & iOS) for file access, firmware updates, and remote control |
Yes: Creators’ App (Android & iOS) for file access, settings, remote control, and setup |
| GPS |
Via a connected smartphone |
Via a connected smartphone |
| Battery |
1x EN-EL15c Rechargeable Lithium-Ion (Approx. 380 shots) |
1x NP-FZ100 Rechargeable Lithium-Ion, 7.2 VDC, 2280 mAh (Approx. 520 shots) |
| Shoe Mount |
1x Hot Shoe |
1x Intelligent Hot Shoe |
| Tripod Mounting Thread |
1x 1/4″-20 Female (Bottom) |
1x 1/4″-20 Female (Bottom) |
| Package Weight |
2.555 lb |
2.48 lb |
| Box Dimensions (LxWxH) |
7.9 x 7.8 x 5.1″ |
10.2 x 7.2 x 6.4″ |
Photography Features Comparison
|
| Sensor Resolution |
Actual: 25.28 Megapixel, Effective: 24.5 Megapixel (6048 x 4032) |
Actual: 34.1 Megapixel, Effective: 33 Megapixel (7008 x 4672) |
| Image Sensor |
35.9 x 23.9 mm (Full-Frame) CMOS |
35.9 x 23.9 mm (Full-Frame) CMOS |
| Sensor Crop (35mm Equivalent) |
Crop Factor: 1x |
Crop Factor: 1x, Additional Modes: 1.5x (Select video modes) |
| Image Stabilization |
Sensor-Shift, 5-Axis, 7.5 Stops, you can link with AF points |
Sensor-Shift, 5-Axis, Traditional |
| Built-In ND Filter |
No |
No |
| Capture Type |
Stills & Video |
Stills & Video |
| Shutter Type |
Mechanical Focal Plane Shutter and Electronic Rolling Shutter |
Mechanical Focal Plane Shutter and Electronic Rolling Shutter |
| Shutter Speed |
1/8000 to 30 seconds, Bulb & Time Mode |
1/8000 to 30 Seconds, Bulb Mode (1/8000 to 1/4 Second in Movie Mode) |
| ISO Sensitivity (Photo) |
Native in Auto Mode: 100 to 64,000 (50 to 204,800 Extended) |
Native in Manual Mode: 100 to 51,200 (50 to 204,800 Extended), Native in Auto Mode: 100 to 12,800 |
| Metering Method |
Center-Weighted Average, Highlight Weighted, Matrix, Spot |
Center-Weighted Average, Highlight Weighted, Multi-Zone, Spot |
| Exposure Modes |
Aperture Priority, Auto, Manual, Program, Shutter Priority |
Aperture Priority, Auto, Manual, Program, Shutter Priority |
| Exposure Compensation |
-5 to +5 EV (1/3, 1/2 EV Steps) |
-5 to +5 EV (1/3, 1/2 EV Steps) |
| Metering Range |
-4 to 17 EV |
-3 to 20 EV |
| White Balance |
Presets: Auto, Cloudy, Color Temperature, Direct Sunlight, Flash, Fluorescent, Incandescent, Preset Manual, Shade
Portrait Persona: Custom Skin WB Tone Selector (Video still both) |
2500 to 9900K, Presets: ATW, AWB, Auto, Cloudy, Color Temperature, Color Temperature Filter, Custom, Daylight, Flash, Fluorescent (Cool White, Day White, Daylight, Warm White), Incandescent, Shade, Underwater |
| Continuous Shooting |
Up to 30 fps at Maximum Resolution |
Up to 10 fps at Maximum Resolution for up to 1000 Frames (Raw, JPEG) |
| Interval Recording |
Yes |
Yes |
| Self-Timer |
2/5/10/20-Second Delay |
2/5/10-Second Delay |
| Aspect Ratio |
1:1, 3:2, 16:9 |
1:1, 3:2, 4:3, 16:9 |
| Image File Format |
HEIF, JPEG, Raw |
HEIF, JPEG, Raw |
| Bit Depth |
14-Bit |
14-Bit |
| Focus Type |
Auto and Manual Focus |
Auto and Manual Focus |
| Focus Mode |
Continuous-Servo AF, Full-Time Servo, Manual Focus, Single-Servo AF |
Continuous-Servo AF, Direct Manual Focus, Manual Focus, Single-Servo AF |
| Autofocus Points |
Phase Detection: 273 |
Phase Detection: 759, Contrast Detection: 425 |
| Autofocus Sensitivity |
-10 to +19 EV |
-4 to +20 EV |
| Built-In Flash/Light |
No |
No |
| Flash Modes |
First-Curtain Sync, Off, Rear Curtain Sync/Red-Eye Reduction, Rear Sync, Red-Eye Reduction, Slow Sync, Slow Sync/Red-Eye Reduction |
Auto, Fill Flash, Hi-Speed Sync, Off, Rear Sync, Red-Eye Reduction, Slow Sync |
| Maximum Sync Speed |
1/200 Second |
1/250 Second |
| Flash Compensation |
-3 to +1 EV (1/3, 1/2 EV Steps) |
-3 to +3 EV (1/3, 1/2 EV Steps) |
| Dedicated Flash System |
iTTL |
TTL |
| External Flash Connection |
Shoe Mount |
Shoe Mount |
Video
|
Raw Video Recording
|
Yes, NRAW |
NA |
| Internal Recording Modes |
H.264/MOV/MP4:
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps
1920 x 1080p at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94/100/120 fps |
H.264/XAVC S-I 4:2:2 10-Bit:
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [240 to 600 Mb/s]
1920 x 1080p at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [89 to 222 Mb/s]
H.265/XAVC HS 4:2:2 10-Bit: |
| Video IS |
IBIS + EVR |
Yes, Gyro |
| External Recording Modes |
8-Bit via HDMI:
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) up to 29.97 fps |
4:2:0 8-Bit via HDMI:
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps |
| Fast-/Slow-Motion Support |
No |
Yes |
| Overheating issues, if any |
No |
Requires V60 above the card, Fixed with the recent firmware updates |
| Log and Gamma Curve |
Not specified |
HDR-HLG, Sony S-Log 2, Sony S-Log 3 |
| Recording Limit |
2-Hour 5-Minute Maximum |
No |
| IP Streaming |
No |
No |
| Built-In Microphone |
Stereo |
Stereo |
| Audio Recording |
MOV, Raw: 24-Bit 48 kHz AAC Audio
MP4: 16-Bit 48 kHz LPCM Audio |
XAVC S: 2-Channel 16-Bit 48 kHz LPCM Audio
MPEG4: 2-Channel AAC LC Audio |
Follow us on our social pages FACEBOOK | TWITTER | INSTAGRAM to get live Camera News + Nikon Rumors 24X7
By admin, on June 18th, 2024

Let’s the comparison of the Nikon Z6 III camera with the Sony A7 IV starting from the design part we do have some major differences let’s find out.
The Sony A7 IV camera uses a 3.69 million-dot electronic viewfinder whereas in the latest Nikon Z6 Mark 3 camera, Nikon has introduced a flagship-level electronic viewfinder with 5.76 million resolution. Not only that, the refresh rate of this particular viewfinder is the best in its class with 120 frames per second as well as the EVF has 4000 nits of brightness units. That indicates you will experience one of the best electronic viewfinders ever introduced in a camera.
Buy Nikon Z6 III from B&H Store | amazon.com

Design and Build
Electronic Viewfinder (EVF)
- Sony A7 IV: 3.69 million-dot resolution.
- Nikon Z6 Mark 3: Flagship-level EVF with a 5.76 million-dot resolution, 120 frames per second refresh rate, and 4000 nits brightness. This provides a superior viewing experience.
Now the second major advantage in the design part of the Nikon Z6 Mark 3 camera we have is the introduction of a full-size HDMI port, so that’s a really very usable tool for professional cinematographers as well as photographers. For those who work in the studio and use their camera in their workflow HDMI cable this is a highly usable upgrade.
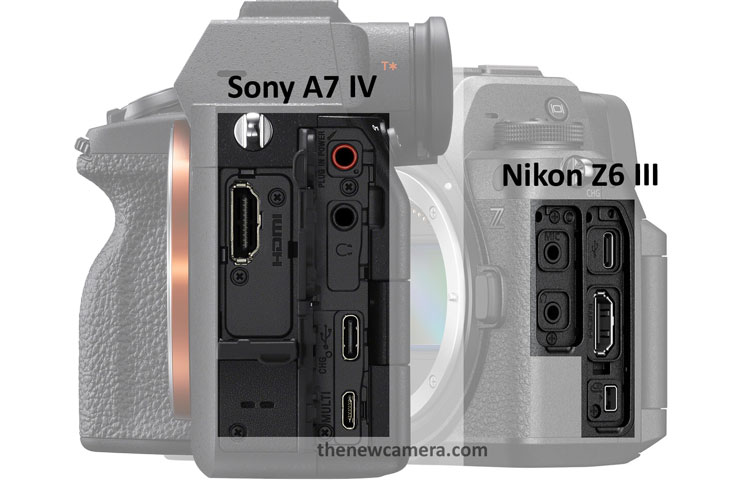

HDMI Port
- Nikon Z6 Mark 3: Features a full-size HDMI port, as well as Sony A7 IV camera, features Full Size HDMI port
Apart from these two features, the rest of the force in both the camera is almost similar. Even if we compare the display screen, the Nikon Z6 Mark 3 camera vari-angle display screen is slightly larger by 2 inches compared to the Sony A7 IV camera. Resolution-wise, the Sony A7 IV camera uses a 1.4 million-dot display unit whereas Z6 Mark 3 camera uses 2.1 million dots display unit, so even though if you compare the electronic viewfinder or the vari-angle display screen in both of the scenarios Z6 Mark 3 camera wins.
Dual vs Triple Card Slot – No Backup option in Nikon Z6 III
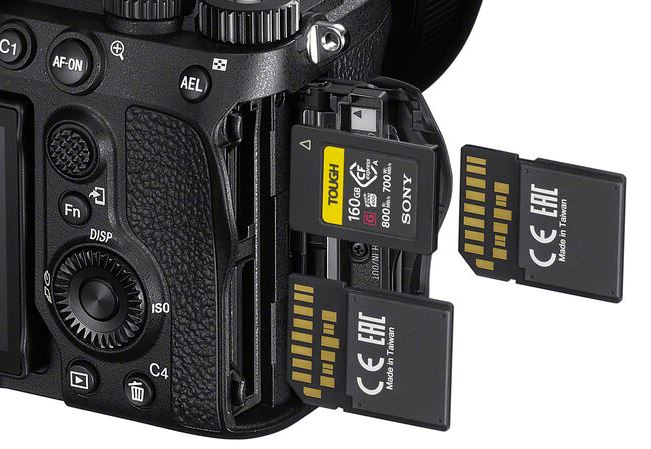
The Sony A7 IV camera carries 3 card slots now why do they have to put 3 different card slots in a single camera says there is no connection between a CF Express Type A card slot and an SD card slot(s), so they have to put two different sets of UHS-II SD card slot and single CF Express Type A card slot at the Sony A7 IV camera so that if you want to create a backup card then you can utilize the two different UHS-II SD card slots in a camera like you use them from DSLR time as a backup card or once the card gets overflow then the camera automatically stores in a different (SD) card so you have all the options available as you generally used the two different card slots in any other camera Pro DSLR Camera, A7 IC also has an extra CF Express to record 4K videos up to 30 frames per second without getting the camera overheated.
The biggest issue with the Nikon Z6 Mark 3 cameras is that you only have two different card slots which act as a single card slot since one is a UHS-II SD card slot and the other is a CF Express Type B card slot now none of these cards are connected so there is no way that you can create a backup card.
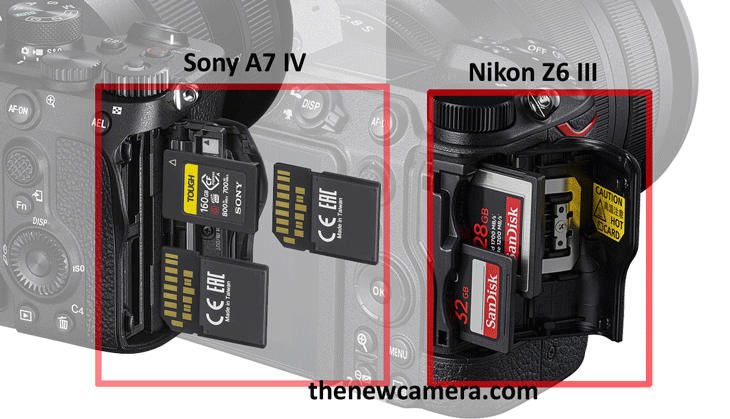
Display Screen
- Sony A7 IV: 1.4 million-dot display unit.
- Nikon Z6 Mark 3: Vari-angle display screen with 2.1 million dots, offering a clearer and larger display.
Now let’s talk about one of the biggest advantages of the Sony A7 IV camera. The Sony A7 IV camera’s battery life is twice as good as in the Z6 Mark 3. With the help of A7 IV you can capture approximately 600 shots and in Z6 Mark 3 with EN-EL 15c battery you’re limited to 380 shots, so approximately with the A7 IV camera, you are getting 220 plus shots in a single charge.
Battery Life
- Sony A7 IV: Approximately 600 shots per charge. That’s an awesome backup, just like DSLR time when u charge and forget
- Nikon Z6 Mark 3: Approximately 380 shots per charge with the EN-EL15c battery. The Sony A7 IV offers better battery life, providing around 220 more shots per charge.
Now it’s time to compare the core specifications of both cameras.
Core Specifications Difference
Sensor and Performance
- Nikon Z6 Mark 3: Newly developed 24.5MP Partially-Stacked CMOS Sensor
- Sony A7 IV: 33MP Full-Frame Exmor R CMOS BSI Sensor (Non Stacked)
Let’s start with the sensor in the latest Z6 Mark 3 camera. We have recently developed partially stacked CMOS sensor with the help of new stacked sensor the camera is able to grab continuous shooting speed up to 120 frames per second in DX mode as well as in full resolution JPEG mode you are able to capture up to 60 frames per second. At the very same time if we calculate the readout speed of the sensor then it ranges between 6.4 milliseconds to 9.4 milliseconds, so overall the readout speed of Nikon Z6 Mark 3 camera sensor is exceptionally well and you will not notice any rolling shutter effect while capturing high frame rate images in your camera. When compared to the Sony A7 IV the continuous shooting speed of the camera is limited to 10 frames per second, which is completely unethical to have such a kind of continuous shooting speed in 2024 in a camera of $2000 price range.
Nikon Z6 Mark III and the Sony A7 IV cameras: comparison of the sensor readout speeds
| Feature |
Nikon Z6 Mark 3 |
Sony A7 IV |
| Sensor Type |
Partially Stacked CMOS |
CMOS |
| Continuous Shooting Speed (DX Mode) |
Up to 120 fps |
Not specified |
| Continuous Shooting Speed (Full Resolution JPEG Mode) |
Up to 60 fps |
10 fps |
| Sensor Readout Speed |
6.4 milliseconds to 9.4 milliseconds |
26.8 milliseconds |
| Rolling Shutter Effect |
Minimal due to fast readout |
More noticeable due to slower readout |
ISO Range
- Nikon Z6 Mark 3: Standard ISO range from 100 to 64,000, expandable from 50 to 204,800. 1 Stop advantage over A7 IV standard ISO range
- Sony A7 IV: Standard ISO range from 100 to 51,200, expandable from 50 to 204,800.
Not only speed when Nikon Z6 Mark 3 camera excels in low light performance and you get extra stops of ISO in this standard ISO zone. The standard ISO range of Nikon Z6 Mark 3 camera starts from 100 to 64,000 and expandable ISO range starts from 50 to 204,800 whereas in Sony A7 IV camera we have standard ISO range that starts from 100 and goes up to 51,200. The expandable ISO range is 50 to 204,800.
| Feature |
Nikon Z6 Mark 3 |
Sony A7 IV |
| Standard ISO Range |
100 to 64,000 |
100 to 51,200 |
| Expandable ISO Range |
50 to 204,800 |
50 to 204,800 |
| Low Light Performance |
Extra stops of ISO in standard range, excels in low light |
Good low light performance, but lower standard ISO range |
Base ISO Test
The resolution advantage is associated with the Sony A7 IV camera. With the Sony A7 IV camera, you can capture 33 megapixel images whereas the Z6 Mark 3 camera is limited to 24 megapixels. If you just compare the 24-megapixel sensor of the Nikon Z6 camera with the Sony A7 IV you can see that the Sony A7 IV camera with the help of a 33-megapixel sensor can extract a little bit more detail in the image when compared to a 24 MP FX-format full-frame sensor of Nikon.
The clear advantage of a Sony A7 IV camera is that you can extract a bit more detail from a given scene, but at the very same time with the Nikon Z6 Mark 3 camera, we do have a higher resolution pixel shift mode.
PIXEL SHIFT Mode in Nikon Z6 Mark III Camera
- Sony A7 IV: 33 megapixels, providing a bit more details
- Nikon Z6 Mark 3: 24 megapixels, but features a pixel shift mode allowing for 96-megapixel images.
With the help of pixel shift mode with Nikon Z6 Mark 3 camera can capture 96 megapixels of image, but we do have a few drawbacks of pixel shift mode. The number one drawback is that the subject has to be still not moving at the very same time you have to place your camera on a tripod and overall the camera is not able to stitch the multiple-shot images you have to take out all the images, put them in a software and it will automatically stitch all together.
Sony A7R Mark IIIa as an option for Pixel Peepers
So yes if you are a high resolution sensor fan then in this particular price you can also get cameras like Fuji XT5 or maybe Sony A7R Mark 3 camera in the very same price range and both of them are approximately 40 megapixels and plus one of my personal favourite cameras is without a doubt Sony A7R Mark 3A even in 2024 so if you are a fan and you want to extract the maximum possible details available in the entire scene then you can go towards these two cameras.
Being said that the sensor does have a little bit less resolution but the low light performance and the readout speed of the Nikon Z6 Mark 3 camera is exceptionally well.
| Feature |
Nikon Z6 Mark 3 |
Sony A7 IV |
| IBIS Stops |
8 stops |
5.5 stops |
| Sensor-Shift IBIS |
Advanced sensor-shift mechanism linked with autofocus points |
Traditional sensor-shift stabilization |
| Slowest Shutter Speed Based on IBIS |
Up to 8 stops slower than standard handheld speeds (approximately 1-second exposure handheld) |
Up to 5.5 stops slower than standard handheld speeds (approximately 0.5-second exposure handheld) |
| Low Light Advantage |
Significant advantage due to 8 stops of IBIS |
Good stabilization but less effective in low light compared to Nikon Z6 Mark 3 |
Additional Features
Image Stabilization
- Nikon Z6 Mark 3: Advanced in-body image stabilization (IBIS) system, offering 8 stops of IBIS. The IBIS is connected to the autofocus points, Advanced AI IBIS algo inside the camera.
- Sony A7 IV: Traditional IBIS system with 5.5 stops of stabilization, not linked to autofocus points.
Now Nikon Z6 Mark 3 camera has an additional advantage for shooting in low light. You already have a low light sensitive full-frame CMOS sensor in construction Mark 3 camera which now pairs up with highly advanced in-body image stabilization system.
The Nikon Z6 Mark 3 camera image stabilization system is coming straight out from Nikon ZF camera. The camera is having 8 stops of IBIS sensor-shift mechanism and one of the most advanced things is the sensor-shift image stabilization system is directly connected with the autofocus point of the camera so as the autofocus point of your camera moves in the frame the sensor-shift image stabilization also shifts and gives you 8 stops of IBIS experience. If you compare with the Sony A7 IV camera sensor-shift stabilization system then it limits to 5.5 stops and it’s kind of traditional IBIS so it is not linked with the points and all that stuff.
Conclusion – Best Camera for Photographers
While the Sony A7 IV offers better battery life and higher resolution, the Nikon Z6 Mark 3 excels in low-light performance, viewfinder quality, display resolution, and continuous shooting speed. The Z6 Mark 3’s advanced HYBRID stabilization system and full-size HDMI port also make it a strong contender for professional use.
Make your Decision on these two FACTORS
1. The Requirement you have for your next camera
2. The Budget Range You Have
TNC Recommendation and Overall Best Camera for Photographers
Nikon Z6 Mark III camera features class-leading core specification and very reasonable price point, I recommend the Nikon Z6 Mark III over the Sony A7 IV camera, the A7 IV now needs an update and lets hope and expect the Sony A7 V will beat the Nikon Z6 III in terms of its core specification as well as price.
If, your requirement is less, you mostly shoot weddings, events, nature, Landscape, or Even portraits and you feel having a bit more details in your image will help you to capture shot with more details, then for sure the Sony A7 IV camera is more recommended to you.
SUPPORT US | Buy Nikon Z6 III from B&H Store | amazon.com
By admin, on April 5th, 2024

You get a slight resolution advantage with the Sony 33mp resolution sensor. Those who are pixel peepers may notice a slight difference when zoomed into 100% scale in the images of Nikon ZF and Sony A7 4 cameras since the ZF camera is limited to 24-megapixel resolution.
WHY NIKON ZF CAMERA IS THE BEST CHOICE FOR PHOTOGRAPHERS
The Nikon ZF is a camera that features extensive manual control over the body and a tank-like, rock-solid body. It feels quite heavy and the extensive manual controls allow you to alter any settings with the help of the dials and controls you have all over the camera body while shooting in manual mode.
| Feature |
Sony A7 4 |
Nikon ZF |
| Resolution |
33mp |
24mp |
| Body |
Standard |
Tank-like, rock-solid |
| ISO Range |
Up to 51,200 |
Up to 64,000 |
| Image Stabilization |
Sensor-shift, weaker in photography mode, stronger in videography |
Advanced 5 stops of sensor-shift with AI algorithm |
| Continuous Shooting |
Up to 10 frames per second |
Up to 15 frames per second |
| High-Resolution Mode |
33 megapixels |
Up to 96 megapixels |
| Low Light Sensitivity |
-4 EV |
-10 EV |
| Lens Mount |
E-Mount | Open Mount |
Nikon Z mount | Open Mount |
| Video Recording |
4K at 60 fps with APS-C crop |
4K at 60 fps with APS-C crop |
| Bit Rates |
600 megabits per second |
340 Mbps for H.265 10-bit video, and 300 Mbps for H.265 8-bit video |
| Image Stabilization in Video |
Desirable, gyro-based |
Standard |
Apart from this, the sensor inside the Nikon ZF camera is ultra-low light-sensitive. The 24-megapixel full-frame sensor features a standard ISO range up to 64,000 whereas the Sony A7 4 camera’s standard ISO range is limited to 51,200. So without a doubt, we will get an extra one-stop advantage in low-light performance from the Nikon ZF camera.
Must see – Best Lenses for Nikon Zf | Sony A7 IV Best lenses
One of the biggest factors that affect the low light performance of the camera is the type of sensor-shift image stabilization system used inside the body. The Nikon ZF camera uses advanced 8 stops of sensor-shift image stabilization technology as well as an artificially intelligent algorithm that moves the autofocus points along with the sensor-shift IBIS technology. So the image stabilization is not always focused at the center of the frame; the center always changes along with the autofocus point in the photography mode. The Sony A7 IV camera IBIS is limited to 5 Stops and traditional IS technology.
Another advantage that we have is the continuous shooting mode of the camera. With the Nikon ZF, you can shoot up to 15 frames per second whereas with the Sony A7 4, you remain limited to 10 frames a second.
|
Sony A74 |
Nikon Zf |
| Autofocus System |
Hybrid PDAF |
Hybrid PDAF with deep learning subject recognition |
| Autofocus Points |
759 |
273 |
| Maximum Low-Light AF Sensitivity (Standardized to f/2, ISO 100) |
-4 EV |
-8.5 EV |
| Standard Flash Sync Speed |
1/250 |
1/200 |
Another big advantage that we have found in the Nikon ZF camera is the low light sensitivity. The ZF camera can shoot up to -10 EV which is in extremely low light conditions whereas the Sony A7 4 camera’s low light capability remains limited to -4 EV.
| High-Resolution Mode |
33 megapixels ONLY – NO HR MODE |
Up to 96 megapixels (requires tripod or studio setup for best results) |
The Sony A7 4 camera’s 33-megapixel advantage is being overshadowed by the Nikon ZF’s multi-shift high-resolution mode which is capable of shooting up to 96 megapixels of resolution. But yes, it is not possible to shoot handheld; you will need a tripod or best to practice the high-resolution mode in a studio setup.
Sony A7 4 versus Nikon ZF, which camera should you buy? VERDICT
So if we combine all the capabilities like the hybrid sensor-shift stabilization system, the high-resolution mode, the better standard ISO range, the capability to shoot higher frame rates, and also advanced or better low light sensitivity, overall the Nikon ZF camera is more recommended to photographers compared to the Sony A7 4.
The lens mount Nikon Z mount is now open and has a variety of options available from third-party lens makers like Sigma and Tamron. So if you are invested in Z mount, you won’t feel that much scarcity of being limited to a specific mount without having any option for third-party lens makers.
Let’s talk about the video comparison of both cameras.
Both cameras are able to shoot videos up to 4K at 60 frames per second, and both of them do have APS-C crop while filming 4K 60p and no crop while recording 4K up to 30 fps.
BIT RATES COMPARED
Let’s compare the bit rates of both the cameras and if you compare the bit rates then it is very clearly evident that Nikon ZF camera lower bit rates (MAX Nikon Zf has a maximum bit rate of approximately 340 Mbps for H.265 10-bit video, and 300 Mbps for H.265 8-bit video. The bit rate depends on the video file type), Sony A7 IV MAX bitrates goes upto 600MPBS. Having slightly higher res sensor can be one of the resons of having such difference since both of them do oversampled 4K videos.
Both cameras record 4:2:2 10-bit internally and in both of them, we have log profiles available for having maximum dynamic range possible.
GYRO-BASED IMAGE STABILIZATION
Now the biggest advantage we have with Sony is its GYRO BASED image stabilization system. Its sensor-shift image stabilization is weak compared to the Nikon ZF camera in photography mode but when we talk about videography, and cinematography then gyro-based image stabilization is way more effective than having a sensor-shift image stabilization system.
LENS BREATHING CORRECTION
Now the most impressive thing that I have seen in the Sony A7 4 camera is lens breathing correction in video. The camera exhibits excellent lens breathing correction while using third-party lenses.
Now we also have an anti-dust shake mechanism inside the Sony A7 4 camera and Nikon should also learn it. The way they have copied this style from Canon, Nikon should also copy this particular style of rotating the sensor either from Sony or Canon because they have to do it otherwise our sensors are not always protected when the lens is unprotected.
Now a full-size HDMI port is available in the Sony A7 4 camera and that’s an amazing thing. Believe me, I really hate having a micro or mini HDMI port in a camera.
OVERHEATING
I have personally used both the camera, Nikon ZF camera handles overheating very well and while using a Sony A7 IV camera you have to use the CF express type A Card or at least V90 to avoid potential early overheating.
BEST CAMERA FOR VIDEO
Sony A7 IV camera is more recommended for video, since if we look at the overall features we get a lot of stuff required for video workflow, but again if you living near the equator, better to invest in Nikon Zf.
Get a Sony A7 IV Camera from Amazon.com | B&H Store
Get a Nikon Zf camera from Amazon.com | B&H Store
By admin, on September 12th, 2023

If you compare the Sony A74 versus the Sony A7C II, let me tell you one thing very clearly. The Sony A7C II camera features the same 33-megapixel full-frame CMOS sensor, Even the AF system of the Sony A7C II camera is much more advanced due to the presence of dedicated artificial intelligence CHIP inside, compared to the Sony A74 camera. Now, we all know that if a baseline product/product with a lower price range has as many special features as its higher-end body, then for sure it will cut off the sales of the A74.
To protect it, Sony added some layers of features and design cannibalization, which now depends upon us. Does this crippling hurt the camera’s core, or can we buy it despite the standard crippling done over Sony A7C II to save the Sony A7 IV sales? Which we will explain in this article.
| Lens Mount |
Sony A7C II |
Sony A7 IV |
| Sensor Resolution |
Actual: 34.1 Megapixel
Effective: 33 Megapixel |
Actual: 34.1 Megapixel
Effective: 33 Megapixel |
| Image Sensor |
35.9 x 23.9 mm (Full-Frame) CMOS |
35.9 x 23.9 mm (Full-Frame) CMOS |
| Image Stabilization |
Sensor-Shift, 7 Stops |
Sensor-Shift, 5.5 Stops |
| Built-In ND Filter |
None |
None |
| Capture Type |
Stills & Video |
Stills & Video |

1. DUAL CARD SLOT
From the design point of view, there is a basic design difference between the two. The Sony A7C II camera has only a single card slot compatible with UHS-II V90 cards, while the Sony A7 IV camera features dual card slots in which you can have UHS-II and CFexpress in the other.
2. Full-size HDMI in Sony A7 IV
The other biggest advantage I see in the Sony A7 IV camera is the presence of a full-size HDMI port, which is missing in the Sony A7C II camera.
3. Anti-Dust Shutter in Sony A7IV
The Sony A7 IV camera also features an anti-dust settling mechanism that covers the sensor and protects it. In the Sony A7C II camera, we have an EFCS shutter, so due to the absence of a fully functional mechanical shutter, we do not have such a feature in this camera.
4. Display Difference
On the display side, the Sony A7 IV has a slightly higher resolution electronic viewfinder (3690k dotvs2360k dot) with a better magnification ratio, as well as a slightly higher resolution LCD screen (1.440k dots vs. 1.030k). The position of the viewfinder is also different in both cameras.
The rest of the things are the body controls. The Sony A7 IV camera has a bit more advanced features, such as a joystick controller on the rear side and a center-placed viewfinder, which generally helps a photographer a bit more in handling a camera and using it while composing a perfect shot


5. Size Difference
As you can see, the Sony A7C Mark II camera is more compact, whereas the A7 IV is a bit bulky. Due to the nature of construction and the type of series they belong to, both have their design interface. So, design-wise, for a professional photographer, undoubtedly the Sony A7 IV camera looks more promising.
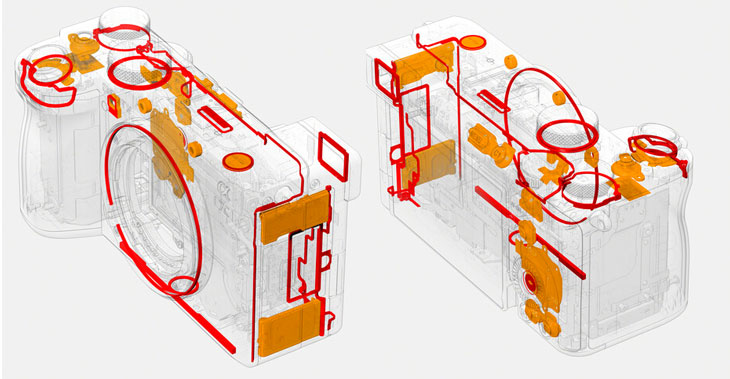
6. Heat Sink
Heat Sink According to initial reports, the heat sink mechanism of the Sony A7C Mark II camera is slightly better at dissipating heat from the body in an outward direction. This is one of the biggest reasons why Sony skipped the CF express card in the A7C Mark II camera. With the use of a UHS-II V90 card (See V90 Cards at Amazon), you can record 4K at all resolutions without any major issues.
Does The Absence Of Full Mechanical Shutter Affect The Performance Of The Camera? It all depends upon your usage. If you want to capture portraits at a very high shutter speed which is somewhere around 1/4000 of a second up to 1/8000 of a second in that very specific scenario most cameras with mechanical shutters are not open to some of these special situations then undoubtedly, the A7C Mark II camera’s EFCS (Electronic Front Curtain Shutter) is very usable.
|
Sony A7C II |
Sony A7 IV |
| Shutter Type |
Electronic Shutter, EFCS |
Electronic Shutter, Mechanical Focal Plane Shutter |
| Anti Dust Shutter |
No |
Yes |
| Shutter Speed |
1/4000 to 30 Seconds
1/8000 to 30 Seconds
1/8000 to 1 Second in Movie Mode |
1/8000 to 30 Seconds
1/8000 to 1/4 Second in Movie Mode |
| Bulb/Time Mode |
Bulb Mode |
Bulb Mode |
| ISO Sensitivity |
Photo
100 to 51,200 in Manual Mode (Extended: 50 to 204,800)
100 to 12,800 in Auto Mode
Video
100 to 51,200 in Manual Mode (Extended: 50 to 102,400)
100 to 12,800 in Auto Mode |
Photo
100 to 51,200 in Manual Mode (Extended: 50 to 204,800)
100 to 12,800 in Auto Mode
Video
100 to 51,200 in Manual Mode (Extended: 100 to 102,400)
100 to 51,200 in Auto Mode |
| Exposure Modes |
Aperture Priority, Auto, Manual, Program, Shutter Priority |
Center-weighted average, Highlight Weighted, Multi-Zone, Spot |
| Continuous Shooting |
Up to 10 fps for up to 44 Frames (Raw) / 1000 Frames (JPEG) |
Up to 10 fps at 33 MP for up to 1000 Frames (Raw) / 1000 Frames (JPEG) |

7. Dedicated AI CHIP
AI Chip The introduction of a dedicated artificial intelligence chip inside this camera has improved its overall performance significantly. Specifically, when we talk about autofocus performance, the 3D object tracking has improved greatly.
Continuous Shooting Speed The biggest improvement that we might see between these two cameras is their ability to track moving subjects while using burst mode. Both feature 10 frames per second continuous burst speed, but now the autofocus performance of the A7C Mark II camera is much improved compared to the Sony A74.
The buffer size of the Sony A74 camera remains larger, one of the biggest reasons being its ability to adopt a CF express-type card slot. The memory of the A7C Mark II camera is slightly limited to 100 frames.
8. IBIS
Image Stabilization With the introduction of the A7 Mark II camera, Sony also introduced a brand new sensor-shift image stabilization mechanism which is very helpful for photographers. Now, the overall IBIS support goes up to 7 stops, and in the Sony A74 camera, it is limited to 5.5 stops.
So if you’re a handheld photographer then undoubtedly, the A7C Mark II camera will help you a lot with its autofocus performance and ability to capture more stable images and footage.
|
Sony A7C II |
Sony A7 IV |
| Internal Recording Modes |
H.265/XAVC HS 4:2:2 10-Bit
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/50/59.94 fps [50 to 200 Mb/s]
H.265/XAVC HS 4:2:0 10-Bit
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/50/59.94 fps [30 to 150 Mb/s]
H.264/XAVC S-I 4:2:2 10-Bit
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [240 to 600 Mb/s]
1920 x 1080p at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [89 to 222 Mb/s]
XAVC S 4:2:2 10-Bit
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [100 to 200 Mb/s]
1920 x 1080p at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [50 Mb/s] |
XAVC HS 4:2:2/4:2:0 10-Bit
3840 x 2160 at 23.98/50/59.94 fps [30 to 200 Mb/s]
XAVC S 4:2:2/4:2:0 8/10-Bit
3840 x 2160 at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [60 to 200 Mb/s]
1920 x 1080 at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94/100/120 fps [16 to 100 Mb/s]
XAVC S-I 4:2:2 10-Bit
3840 x 2160 at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [240 to 600 Mb/s]
1920 x 1080 at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [89 to 222 Mb/s] |
| External Recording Modes |
4:2:2 10-Bit via HDMI
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps
1920 x 1080p at 23.98/50/59.94 fps
1920 x 1080i at 50/59.94 fps
4:2:0 8-Bit via HDMI
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps
1920 x 1080p at 23.98/50/59.94 fps
1920 x 1080i at 50/59.94 fps |
4:2:2 8/10-Bit via HDMI
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps
HD (1920 x 1080p) at 23.98/50/59.94 fps
HD (1920 x 1080i) at 50/59.94 fps |
| AI AUTO FRAMING |
Yes |
NO |
| Enhanced AI AF |
Yes (Dedicated AI CHIP) |
NO |
| IBIS VIDEO |
7 STOPS / GYRO Support |
5.5 Stops Gyro Support |
| Gamma Curve |
HDR-HLG, Sony S-Log 2, Sony S-Log 3 |
S Cinetone, Sony S-Log 3 |
| Recording Limit |
None |
None |
| Broadcast Output |
NTSC/PAL |
NTSC/PAL |
| IP Streaming |
MJPEG, UVC/UAC
3840 x 2160 at 12.5p, 14.99p, 25p, 30p
1920 x 1080 at 25p, 30p, 50p, 60p
1280 x 720 at 25p, 30p |
MJPEG, UVC/UAC
3840 x 2160 at 12.5p, 14.99p, 25p, 30p
1920 x 1080 at 25p, 30p, 50p, 60p
1280 x 720 at 25p, 30p |
| Built-In Microphone Type |
Stereo |
Stereo |
| Audio Recording |
XAVC S: 2-Channel 16-Bit 48 kHz LPCM Audio
MPEG4: 2-Channel AAC LC Audio |
2-Channel 16-Bit 48 kHz LPCM Audio |
9. Videographics Difference Between Both The Cameras
Resolution-wise both cameras feature exactly the same video resolution, Record in 10-bit 4:2:2 using the advanced XAVC S-I format for consistent performance and quality at bitrates up to 600 Mb/s.
With the introduction of the AI chip in Mark II camera tracking performance has improved significantly in videography. The camera is able to track moving subjects from afar and even eye detection is now much more accurate even in animals and insects while you are creating your video.
10. User Uploadable LUT and AI Framing
Other big differences like in professional cameras we have user-uploadable LUTs (Look-Up Tables). With this feature, you are able to control output in a much better way optimizing your workflow as desired.
Auto Framing With introduction of dedicated AI chip we also have an opportunity for artificial intelligent auto framing.
Enhanced Heat Sink Unit As I have said in this post, The A7C Mark II camera’s heat dissipation system is now much more improved and distributes heat effectively.
11. Price Difference vs Features Difference
If you compare the price and specifications we are getting with the Sony A7C Mark II camera it’s much more compared to the set of features that we are getting with the A74. If you want to have the same set of features with the A74 camera body you have to wait for the Sony A75 camera announcement. Otherwise, we highly recommend you get the Sony A7C Mark II camera while looking at its core specification and price ratio.
Sony A7C II Body Price $2198 B&H STORE | AMAZON.com
Sony A7 IV Body Price $2498 B&H STORE | AMAZON.com
By admin, on March 31st, 2023

Sony ZV-E1 vs Sony A74 – let’s have a deeper drive and find out which camera is best for you. The biggest advantage associated with the Sony 74 camera is its body design.
Also, see – Sony ZV-E1 vs Sony FX30
BODY DESIGN
If you are a photographer and doing a long photography assignment that will take approx 3 to 4 hours or maybe you are a kind of wedding photographer or event shooter in those specific scenarios you need to have a camera that perfectly fits in your hand and you feel very comfortable to hold. In those specific situations when you have to work for a very long period Sony A74 camera body design is super perfect without a single doubt. When u have an extra slim camera in ur hand u have to balance it always feels like ur losing the grip. So, for photographers, it’s very important to select a camera with the perfect body design.
- Sony ZV-E1 Best Lenses for Content Creators – B&H Store | Amazon.com
- Sony ZV-E1 Best Lenses for Cinematographers – B&H Store | Amazon.com
Sony ZV-E1 camera is more compact, has a sleek body without any electronic viewfinder, and also the grip is very similar to the entry-level APS-C bodies. So, it is made like to be placed in a gimbal or a selfie stick to record the videos perfectly. The Intention of the design is not favorable for photographers, there yes you can click some occasional pics but it is not made for that.
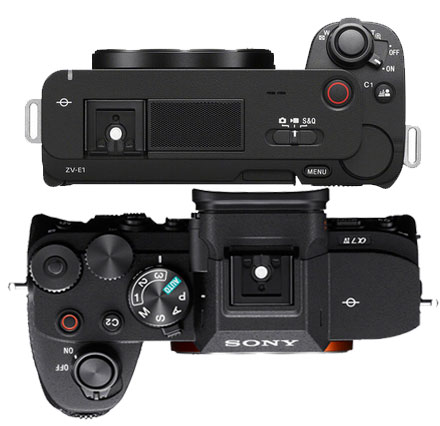

MORE RESOLUTION = MORE DETAILS
Another Major advantage associated with the Sony A74 camera is the higher resolution 33-megapixel full-frame CMOS sensor. If you are a photographer you feel very limited while using a 12-megapixel full-frame sensor and snapping pics. if you have to do a digital crop the 12-megapixel image will not allow you to do that.
The Biggest advantage that I feel in using a higher resolution camera is that you get more and more details while zooming ( @100 % scale) if you are a pixel-peeper. if you like to see more details in a given frame of a scene, it’s highly recommended that photographers use your higher resolution sensor instead of having a lower resolution as we have in the Sony ZE-V1 camera
BEST CAMERA FOR PHOTOGRAPHERS
Design-wise and based on the type of sensor being used inside both the camera it’s highly recommended that if you are a photographer you should go with a Sony A74 camera at the same time if you are more into videography if you are more into content creation and you shoot occasionally few pics you can use the Sony ZV-E1 camera. Yes, you can use your A74 camera as a backup camera for shooting your pics. but it cannot be used as a primary photographic tool if you are into professional work out there.

BEST CAMERA FOR RECORDING VIDEO
In the video part without having a single doubt in your head you should pick Sony’s latest ZV-E1 camera.
The reason behind that the camera can shoot for case 60 frames per second without any crop whereas we all know with the Sony is A74 camera, we have to face APS-C crop, or if you say with some butter that we are shooting in a super 35 mm format while using A74 in 4k 60p mode,
With Sony ZV- E1 camera we do not have any of such used even the camera allows you to suit 4K 120 FPS maybe the firmware update which is about to arrive in June 2023 the cost you a bit that’s another matter but you can suit 4K 120 happiest with only 10% crop which is not similar to the A7 4K 60p super 35 mm all that crop.
now the other biggest advantage that you will enjoy in Sony’s latest ZV-E1 camera is the introduction of a dedicated artificial intelligence chip that was the first scene in Sony’s A7 are 5 camera announcement now the chip has been improved to perform better functionality at the same time new features also being introduced inside this camera.
Overall if you are into content creation videography cinematography in any way you are associated with a video you must buy the latest Sony Z1 camera instead of the Sony is 74
Sony ZV-E1 vs. Sony A7 IV – Best Vlogging Camera for 2023
| Lens Mount |
Sony ZV-E1 |
Sony A74 |
| Sensor Resolution |
Effective: 12.9 Megapixel (4240 x 2832) |
Actual: 34.1 Megapixel
Effective: 33 Megapixel |
| Sensor Type |
35.6 x 23.8 mm (Full-Frame) CMOS |
35.9 x 23.9 mm (Full-Frame) CMOS |
| Image Stabilization |
Sensor shift, 5-Axis |
Sensor-Shift, 5-Axis |
| Built-In ND Filter |
None |
None |
| Capture Type |
Stills & Video |
Stills & Video |
Exposure Control
| Shutter Type |
Electronic Shutter |
Electronic Shutter, Mechanical Focal Plane Shutter |
| Shutter Speed |
1/8000 to 30 Second
1/8000 to 1 Second in Movie Mode |
1/8000 to 30 Seconds |
| ISO Sensitivity |
Photo
80 to 102,400 (Extended: 80 to 409,600) |
Photo
100 to 51,200 (Extended: 50 to 204,800)
Video
100 to 51,200 (Extended: 100 to 102,400) |
| Metering Method |
Center-Weighted Average, Highlight Weighted, Multiple, Spot |
Aperture Priority, Manual, Program, Shutter Priority |
| Metering Range |
3 to 20 EV |
-3 to 20 EV |
Video Details – Comparison of Resolution and frame rates
| Internal Recording Modes |
RawXAVC HS 4:2:0 10-Bit
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 50/59.94 fps [45 to 150 Mb/s]
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98 fps [30 to 100 Mb/s]
RawXAVC HS 4:2:2 10-Bit
3840 x 2160 at 50/59.94 fps [100 to 200 Mb/s]
3840 x 2160 at 23.98 fps [50 to 100 Mb/s]
RawXAVC S 4:2:2 8-Bit
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 50/59.94 fps [100 to 200 Mb/s]
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 25/29.97 fps [140 Mb/s]
RawXAVC S 8-Bit
1920 x 1080p at 100/120 fps [60 to 100 Mb/s]
1920 x 1080p at 50/59.94 fps [25 to 50 Mb/s]
RawXAVC S 10-Bit
1920 x 1080p at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [50 Mb/s]
RawXAVC S-I 10-Bit
3840 x 2160 at 59.94 fps [600 Mb/s]
3840 x 2160 at 50 fps [500 Mb/s]
3840 x 2160 at 29.97 fps [300 Mb/s]
3840 x 2160 at 25 fps [250 Mb/s]
3840 x 2160 at 23.98 fps [50 Mb/s]
1920 x 1080p at 59.94 fps [222 Mb/s]
1920 x 1080p at 50 fps [185 Mb/s]
1920 x 1080p at 29.97 fps [111 Mb/s]
1920 x 1080p at 25 fps [93 Mb/s]
1920 x 1080p at 23.98 fps [89 Mb/s] |
H.265/XAVC HS 4:2:2 10-Bit
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/50/59.94 fps [50 to 200 Mb/s]
H.265/XAVC HS 4:2:0 10-Bit
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/50/59.94 fps [30 to 150 Mb/s]
H.264/XAVC S-I 4:2:2 10-Bit
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [240 to 600 Mb/s]
1920 x 1080p at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [89 to 222 Mb/s]
XAVC S 4:2:2 10-Bit
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [100 to 200 Mb/s]
1920 x 1080p at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [50 Mb/s]
XAVC S 4:2:0 8-Bit
UHD 4K (3840 x 2160) at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94 fps [60 to 150 Mb/s]
1920 x 1080p at 23.98/25/29.97/50/59.94/100 fps [16 to 100 Mb/s] |
|
|
|
Interface
| Media/Memory Card Slot |
Slot 1: CFexpress Type A / SD (UHS-II)
Slot 2: SD/SDHC/SDXC (UHS-II) |
Single Slot: SD/SDHC/SDXC (UHS-II) |
| Video I/O |
1 x HDMI Output |
1X HDMI
|
| Audio I/O |
1 x 1/8″ / 3.5 mm TRS Stereo Headphone Output
1 x 1/8″ / 3.5 mm TRS Stereo Microphone Input |
1 x 1/8″ / 3.5 mm TRS Stereo Microphone Input
1 x 1/8″ / 3.5 mm TRS Stereo Headphone Output |
| Power I/O |
1 x USB-C Input/Output |
1 x USB-C Input |
| Other I/O |
1 x Sony Multi/Micro-USB Input/Output (Shared with Remote Input)
1 x USB-C (USB 3.2 / 3.1 Gen 2) Input/Output (Shared with Power Input) |
1 x USB-C (USB 3.2 / 3.1 Gen 1) Data Input/Output (Shared with Power Input)
1 x Sony Multi/Micro-USB Control |
| Wireless |
Wi-Fi, Bluetooth |
Wi-Fi, Bluetooth |
| Mobile App Compatible |
No
*As of October, 2021: Check with manufacturer for the most up-to-date compatibility |
Yes
*As of March, 2023: Check with manufacturer for the most up-to-date compatibility |
| Global Positioning (GPS, GLONASS, etc.) |
None |
None |
Monitor
| Size |
3.0″ |
3.0″ |
| Resolution |
1,036,800 Dot |
1,036,800 Dot |
| Display Type |
Articulating Touchscreen LCD |
Free-Angle Tilting Touchscreen LCD |
| EVF |
NO |
YES |
Also, see – Sony ZV-E1 vs Sony FX30
- Sony ZV-E1 Best Lenses for Content Creators – B&H Store | Amazon.com
- Sony ZV-E1 Best Lenses for Cinematographers – B&H Store | Amazon.com
|
KEEP THIS BLOG ALIVE - Support New Camera Buy Canon Lenses, Buy Music CD or Digital Camera at amazon it helps this site, and you do not pay anything extra, it is just a way to help support this site.

|


























