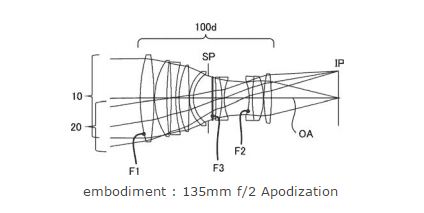
 Before we begin you must know that till now Canon doesn’t have lens with Apodization Filter. In past Canon applied a patent for Canon 135mm F2.8 and 180 F3.5 Lens with Apodization Filter., today new and refreshed 135mm lens appeared with bright F2 aperture and Apodization Filter.
Before we begin you must know that till now Canon doesn’t have lens with Apodization Filter. In past Canon applied a patent for Canon 135mm F2.8 and 180 F3.5 Lens with Apodization Filter., today new and refreshed 135mm lens appeared with bright F2 aperture and Apodization Filter.
The Apodization Filter helps you to get more smooth and creamy bokeh compared to a conventional lens.
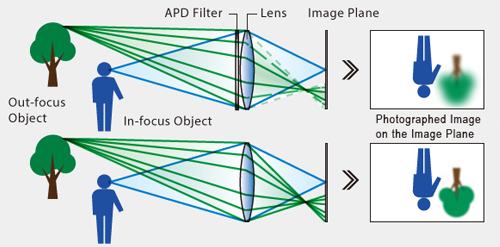 From the image above you can see the work of Apodization Filter inside the lens. Filter creates pleasing and creamy bokeh .
From the image above you can see the work of Apodization Filter inside the lens. Filter creates pleasing and creamy bokeh .
Patent publication number 2016-218444
Release date 2016.12.22
Application date 2015.5.20
Example
Focal length 130.98
F number 2.06
Field of View 9.38
Image height 21.64
Lens total length 159.05
BF 53.99
Canon patent
Even when there is vignetting, a good blurred image at all angle of view
As we have said Canon also Canon 135mm F2.8 and 180 F3.5 Lens with Apodization Filter in 2012, Details below

Patent literature, and abstract · self-interpretation
Patent publication number 2012-128151
Release date 2012.7.5
Application date 2010.12.15
Example 1
Focal length f = 135.0 – 137.2 mm
Fno. 2.83 – 3.90
Half-picture each 9.1 deg.
Image height 21.60 mm
Lens total length 150.0 – 186.7 mm
BF 47.4 – 80.7 mm
Lens construction 7 groups 10 sheets
1 UD glass
Maximum shooting magnification 0.25 times
Example 6
Focal length f = 180.0 – 179.1 mm
Fno. 3.50 – 4.00
Half of each figure 6.9 deg.
Image height 21.60 mm
Lens total length 199.8 – 218.0 mm
BF 70.0 – 89.8 mm
Lens configuration 7 groups 11 pieces
1 UD glass
Maximum shooting magnification 0.11 times
How to see out focus (Bokeh) is important
Apodization filter
Filter whose transmittance decreases in the peripheral part
Addition of intensity distribution to luminous flux
Bokeh’s outline becomes beautiful
Variable apodization element
If the shape of the interface is a liquid with the same refractive index, aberration variation does not occur
It is difficult to make the refractive powers and the Abbe numbers of the two liquids the same
Canon ‘s patent
Shape variable element
By changing the shape of the interface by applying voltage
Obtain apodization effect
Change refractive power and Abbe number
Reduce various aberrations in shape change
Optimize the absorption coefficient by devising the material to moderate the curvature of the interface and suppress the occurrence of aberrations
Reverse the amount of chromatic aberration of two materials (liquid etc.) and cancel it
Suppresses the difference in refractive index and Abbe number of two materials (liquid etc.)
Overall extension (with floating)






