Join More Than 50,000+ Subscribers and get latest camera news and rumors
NEW CAMERA VIDEOS ON YOUTUBE
|
By admin, on April 29th, 2013

Panasonic LF1 Specification Comparison vs Canon G15 vs Nikon P7700 vs Panasonic LX7, we have created a common table for all the popular pro compact comparison. take a look,
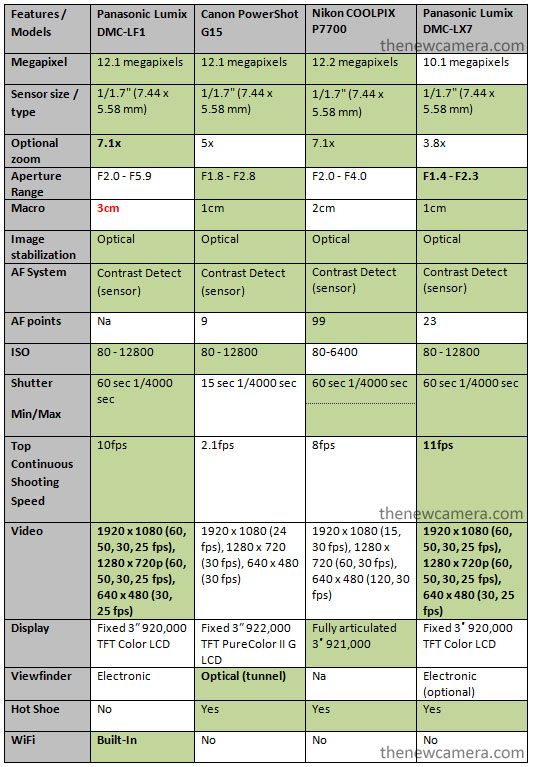
The week point of LF1 is its Macro range (3cm) and its price $499, Nikon P7700 have limited ISO range and video mode but offers excellent core specification @ $389. Which one you will buy? share your thoughts with us.
Take a look at the latest price / Buy your fav camera from Amazon.
By admin, on April 29th, 2013
Panasonic LF1 Samples is available now, take a look at the samples below. Buy Panasonic LF1 from Amazon | B&H
 1/30 sec, F 2, ISO Sensitivity 80.  1/13 sec, F 2, ISO Sensitivity 80.  1/13 sec, F 2, ISO Sensitivity 80
By admin, on April 24th, 2013
Panasonic G6 Sample images are available now, G6 features same sensor as Panasonic GH2, See the Panasonic G6 announcement page | Pre-order / Buy Panasonic G6 from Amazon
Click to en-large images
 Shutter 1/60 sec, F 7.1, ISO 160 Shutter 1/60 sec, F 7.1, ISO 160
Continue reading Panasonic G6 Sample Images
By admin, on April 24th, 2013

Panasonic G6 features 16.1 megapixels M4/3 sensor same as GH2, ISO range upto 25600, Contrast based AF system, Full HD recording at 60fps, on the rear side we have Fully articulated 3″ inch high resolution Touch display.
Major Features
- 16MP Live MOS Sensor (Same as GH2)
- Venus Engine Image Processor
- Micro Four Thirds Standard
- 3.0″ 1,040k-Dot Tilting Touchscreen LCD
- Full HD 1080i Video Recording at 60fps
- 20fps Continuous Shooting Rate
- Built-In Wireless and NFC Connectivity
The Panasonic G6 also features WiFi connectivity with NFC (Near Field Communication) technology, G6 is available in black, white or silver to match the user’s preference. The Price of G6 is approx $749, available in stores from June 21, 2013.
Pre-order/Buy Panasonic DMC G6 Mirrorless Camera from Amazon || B&H
Continue reading Panasonic DMC-G6 Announced
By admin, on April 20th, 2013

Its almost confirmed that Panasonic LF1 (Pro-Compact Camera) and G6 coming next week, Panasonic may also re-new 14-140mm Lumix G Vario lens. The Panasonic LF1 will feature fixed zoom lens and built-in viewfinder. more info coming soon…
source-digicaminfo
By admin, on April 11th, 2013

Panasonic GF6 Sample Images are now available, take a look at the resized samples below, and some gallery link of other website.
Buy Panasonic GF6 from Amazon | B&H
 ISO 160, 4 sec, F 7.1  ISO 160, 6 sec, F 7.1  ISO 160, F 5.1, 1/800 sec
By admin, on April 9th, 2013
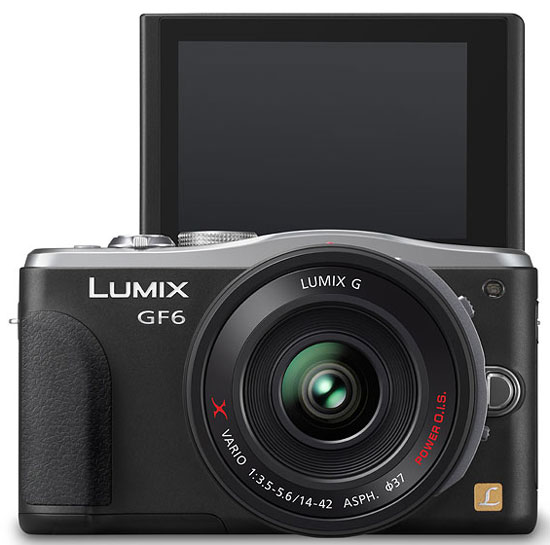

The rumored Panasonic GF6 finally announced, the camera features 16 Mp sensor, captures Full HD cideos at 60i, ISOISO 25600(Extended), movable screen for easy self portraits, WiFi connectivity, compact-camera style zoom lever, also features Near Field Communication (NFC) that allows setup of Wi-Fi connections with compatible smartphones and tablets.
Buy Panasonic GF6 from Amazon | B&H
Panasonic GF6 Major Features
- New 16.00–megapixel Live MOS Sensor
- ISO 25600(Extended)
- High precision Light Speed AF system
- 1920 x 1080 at 60i (NTSC) / 50i (PAL)
- Full-time AF and tracking AF is available in video recording
- Wi-Fi® connectivity featuring NFC (Near Field Communication) technology
- 3.0-inch large approx.180°tiltable monitor
Combination of the new Live MOS Sensor and the Venus Engine achieves ISO3200 (Auto) and max. ISO 25600 (Extended). The Low Light AF in DMC-GF6 gains higher performance in such as moonlight even without AF assist lamp to set focus on the subject more quickly and more precisely.
Another new in-camera function is Clear Retouch, which makes it is possible to erase unwanted objects or figures in an image by just tracing over them on monitor with a fingertip. They naturally disappear without destroying the image.
Continue reading Panasonic GF6 Announced
|
KEEP THIS BLOG ALIVE - Support New Camera Buy Canon Lenses, Buy Music CD or Digital Camera at amazon it helps this site, and you do not pay anything extra, it is just a way to help support this site.

|


















